Small Things Make a Big Difference:Conductive Cross-Linking Sodium Alginate@MXene Binder Enables High-Volumetric-Capacity and High-Mass-Loading Li–S Battery
摘要
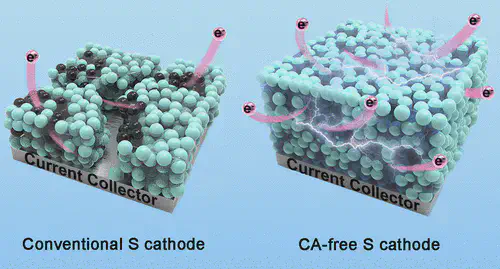
Binders are crucial for maintaining the integrity of an electrode, and there is a growing need for integrating multiple desirable properties into the binder for high-energy batteries, yet significant challenges remain. Here, we successfully synthesized a new binder by cross-linking sodium alginate (SA) with MXene materials (Ti3C2Tx). Besides the improved adhesion and mechanical properties, the integrated SA@Ti3C2Tx binder demonstrates much improved electronic conductivity, which enables ruling out the fluffy conductive additive from the electrode component with enhanced volumetric capacity. When SA@Ti3C2Tx is used to fabricate sulfur (S) cathodes, the conductive-additive-free electrode demonstrates extremely high capacity (1422 mAh cm–3/24.5 mAh cm–2) under an S loading of 17.2 mg cm–2 for Li–S batteries. Impressively, the SA@Ti3C2Tx binder shows remarkable feasibility in other battery systems such as Na–S and LiFePO4 batteries. The proposed strategy of constructing a cross-linking conductive binder opens new possibilities for designing high-mass-loading electrodes with high volumetric capacity.