A skin-mimicking multifunctional hydrogel via hierarchical, reversible noncovalent interactions
摘要
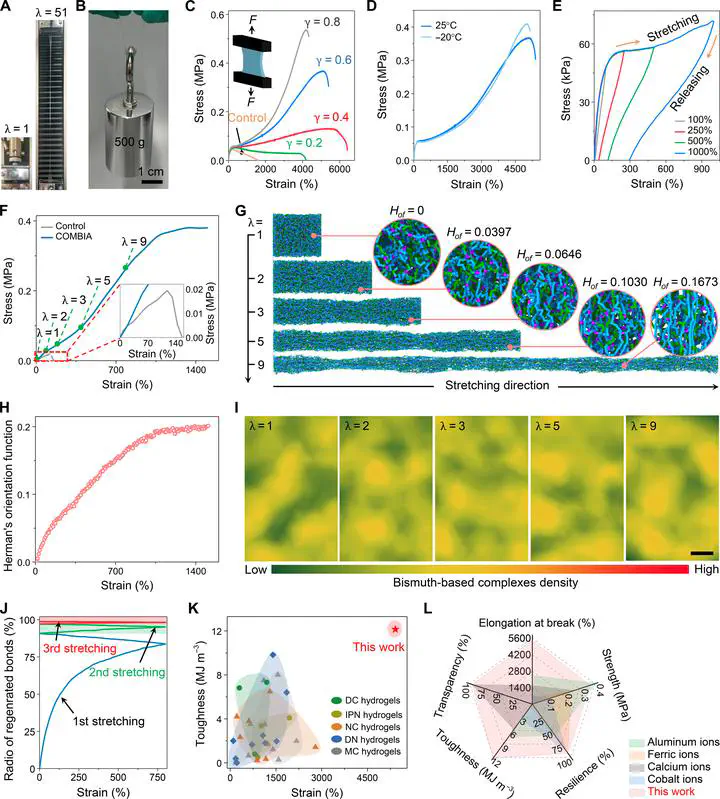
Artificial skin is essential for bionic robotics, facilitating human skin–like functions such as sensation, communication, and protection. However, replicating a skin-matched all-in-one material with excellent mechanical properties, self-healing, adhesion, and multimodal sensing remains a challenge. Herein, we developed a multifunctional hydrogel by establishing a consolidated organic/metal bismuth ion architecture (COMBIA). Benefiting from hierarchical reversible noncovalent interactions, the COMBIA hydrogel exhibits an optimal combination of mechanical and functional properties, particularly its integrated mechanical properties, including unprecedented stretchability, fracture toughness, and resilience. Furthermore, these hydrogels demonstrate superior conductivity, optical transparency, freezing tolerance, adhesion capability, and spontaneous mechanical and electrical self-healing. These unified functions render our hydrogel exceptional properties such as shape adaptability, skin-like perception, and energy harvesting capabilities. To demonstrate its potential applications, an artificial skin using our COMBIA hydrogel was configured for stimulus signal recording, which, as a promising soft electronics platform, could be used for next-generation human-machine interfaces.